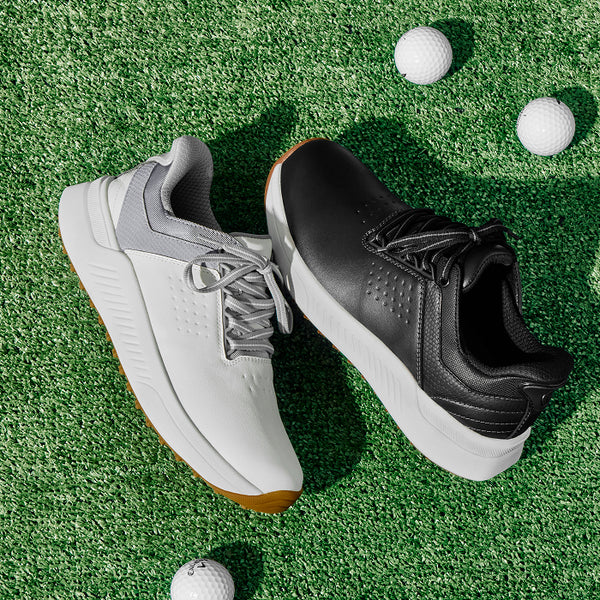
Demonstrated Pain Relief
In a randomized controlled trial conducted at Baylor College of Medicine, Orthofeet shoes were shown to significantly reduce chronic foot pain compared to participants' regular footwear.
- Participants experienced an average 25% reduction in chronic foot pain.[1]
- The study evaluated outcomes after participants wore Orthofeet shoes for a multi-week period.
These findings support Orthofeet’s therapeutic design approach, aimed at relieving foot discomfort through biomechanically engineered footwear.
Learn More


Biomechanically Improved Stability
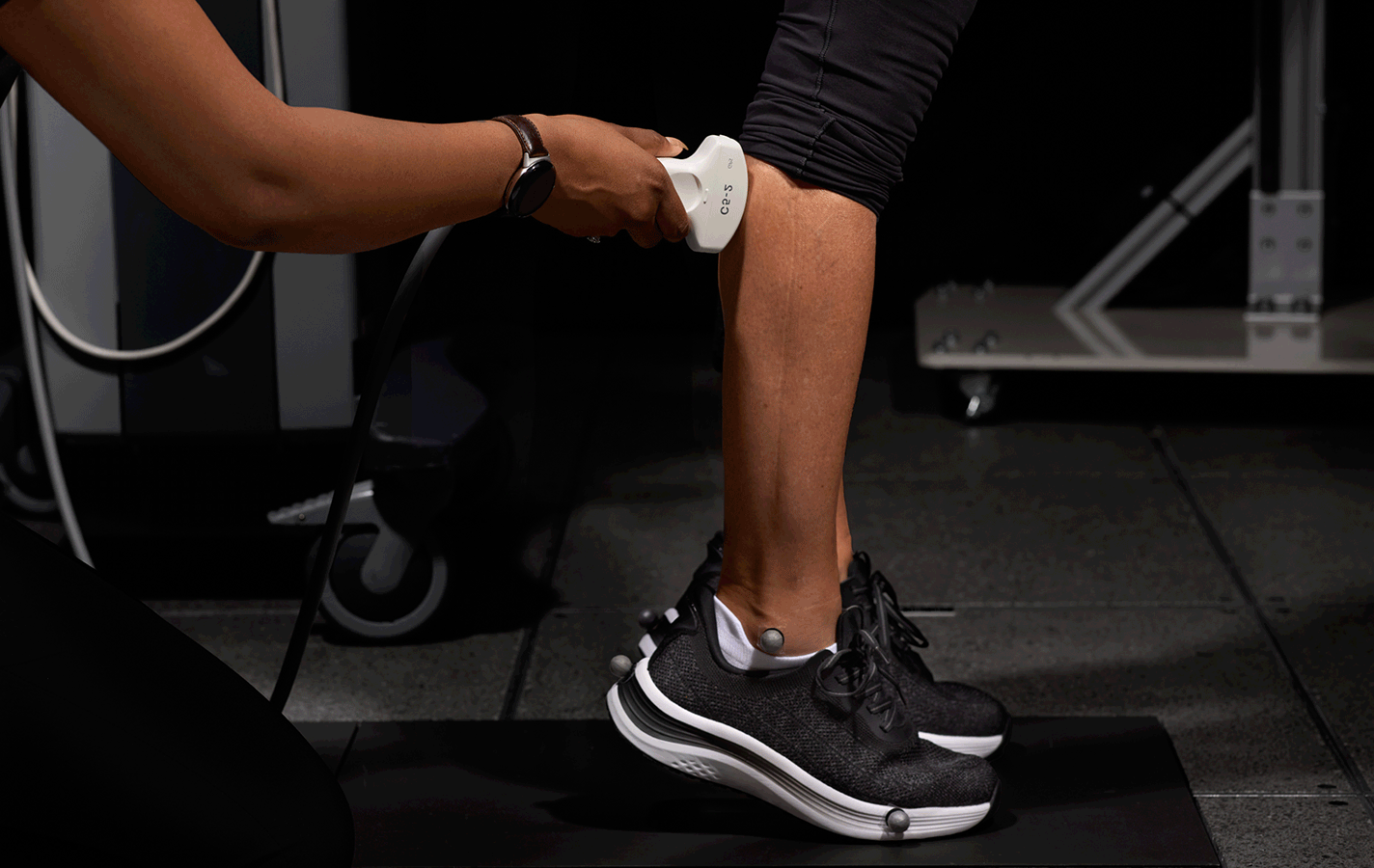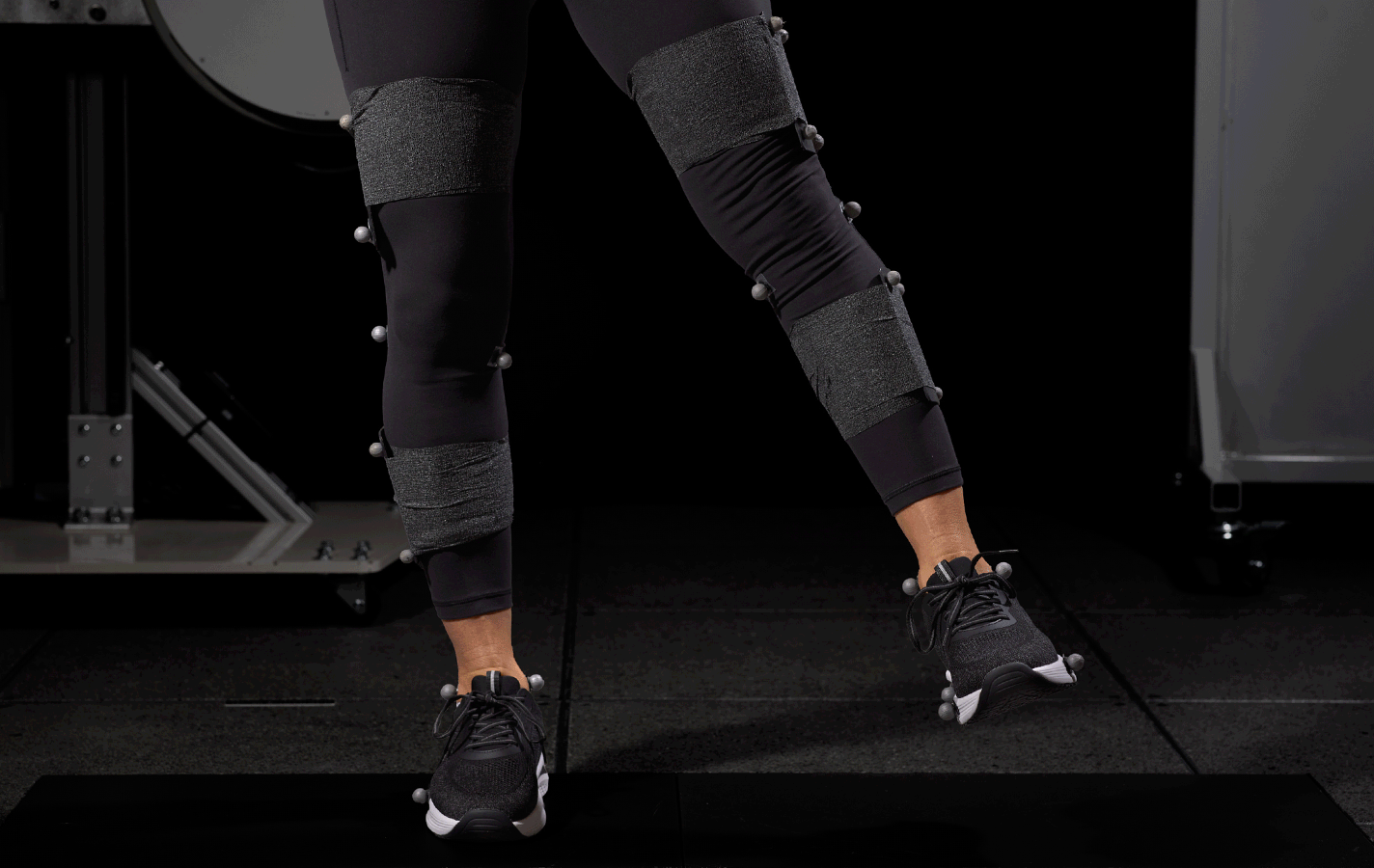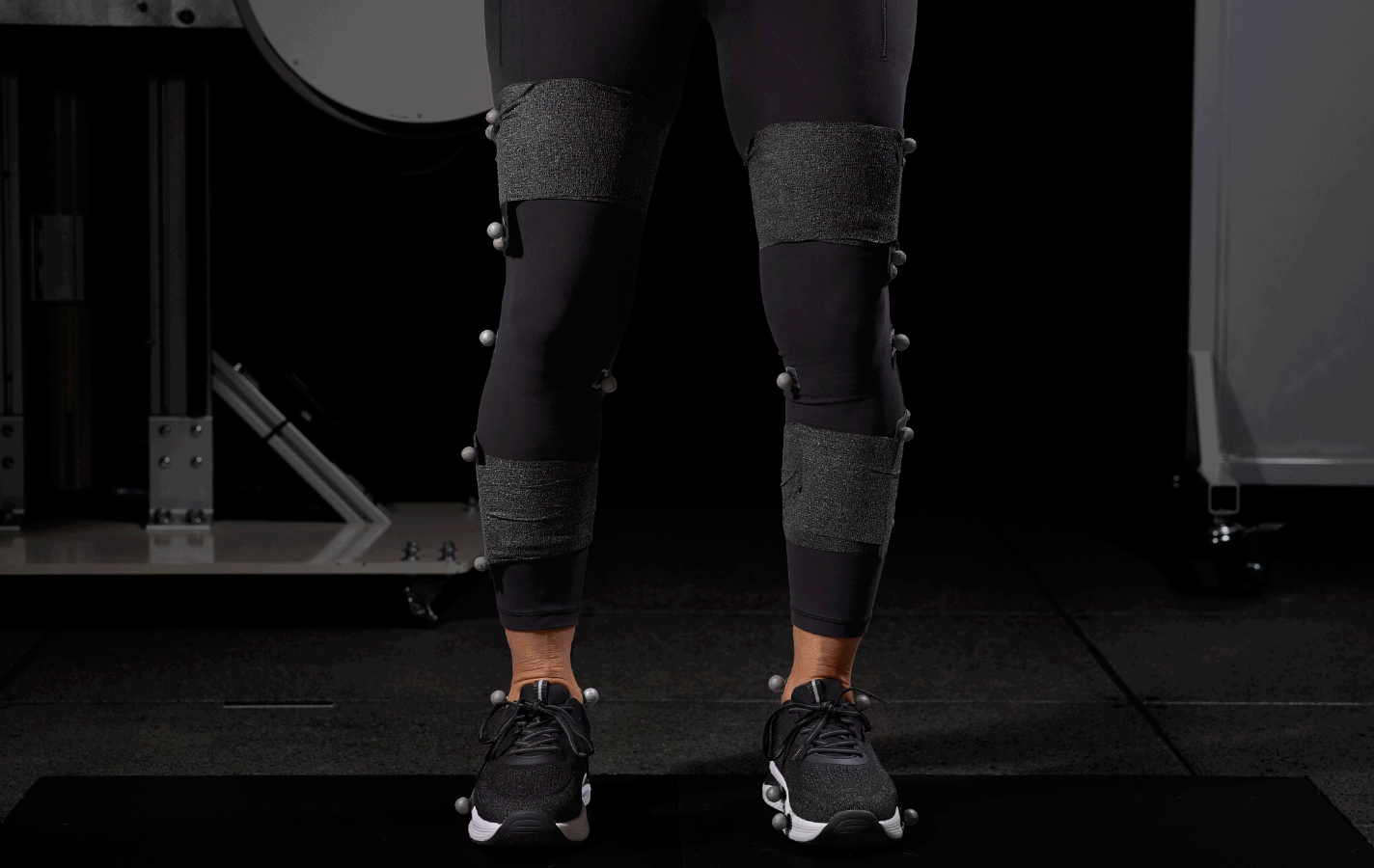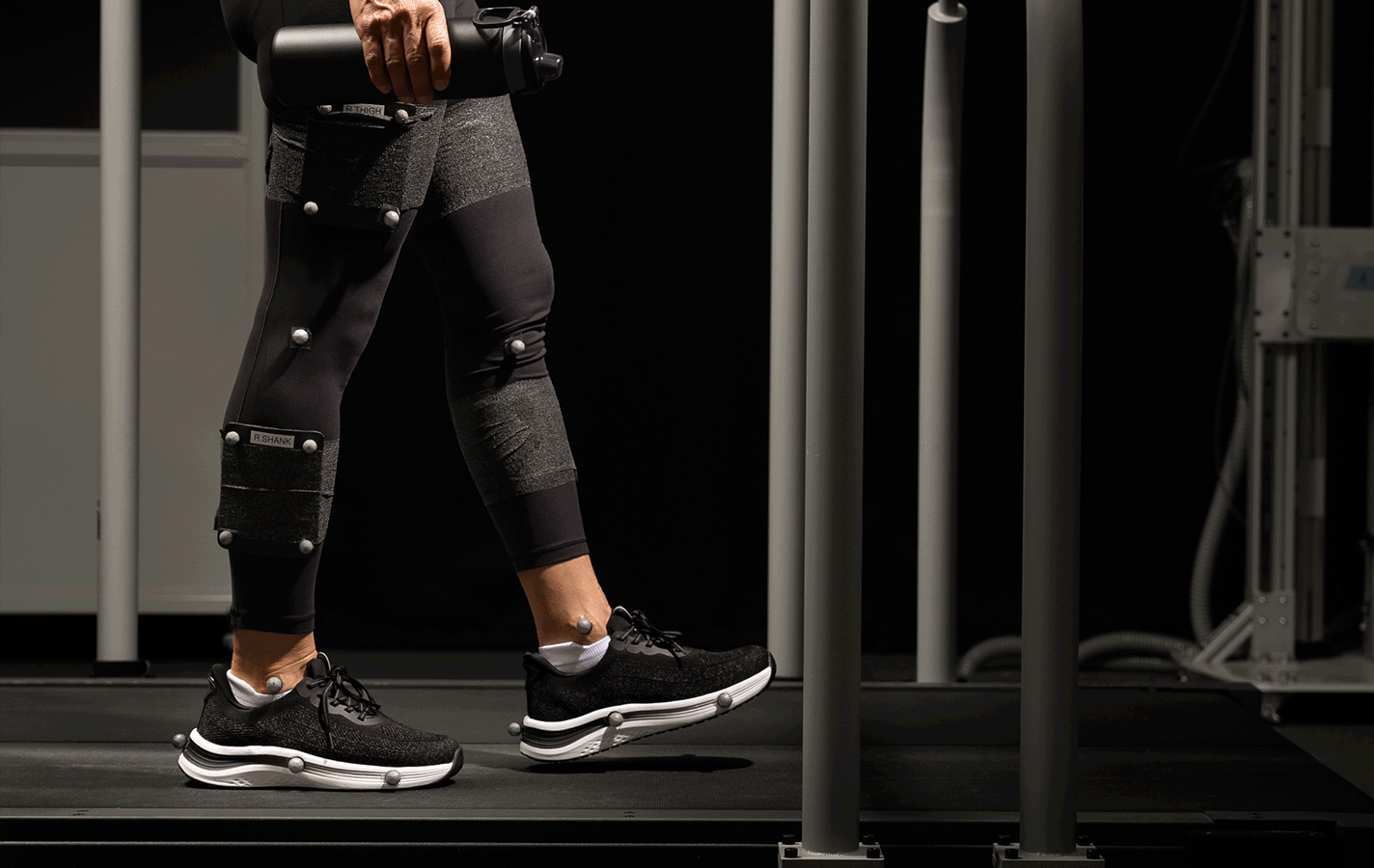
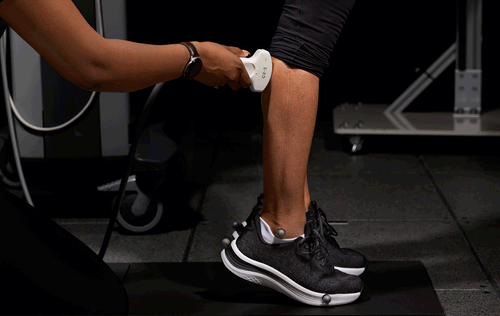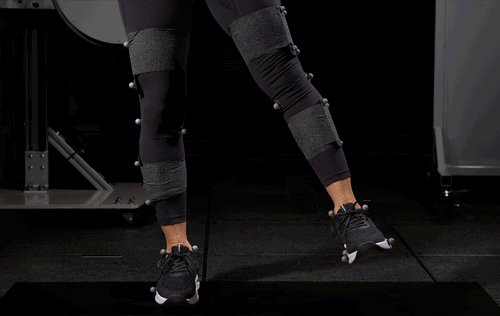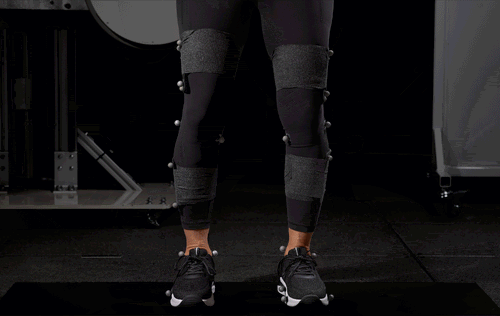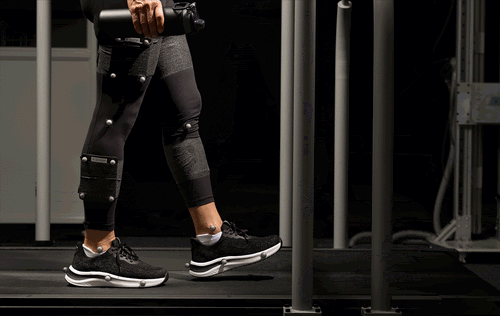
In collaboration with the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Applied Biomechanics Laboratory, our shoes were put through extensive biomechanical testing and the results speak for themselves:
- 15% reduction in mediolateral (side-to-side) sway during balance tests, indicating significantly improved postural control.
- 18% more ankle stability during challenging walking tasks, including treadmill perturbation tests.
Participants reported smoother movement, enhanced balance, and greater stability, validating Orthofeet’s commitment to performance-backed comfort.[2]
Learn More


Increased Daily Activity
A separate clinical study conducted at Baylor College of Medicine evaluated the impact of Orthofeet therapeutic footwear on daily physical activity among older adults with chronic foot pain.
- Participants wearing Orthofeet shoes showed a 15% increase in overall activity levels[3].
- On average, participants took nearly 700 additional steps per day.
- This translated to an increase in daily energy expenditure of 177 kcal.
The study demonstrates that therapeutic footwear may play a meaningful role in promoting mobility and increasing physical activity in populations with foot pain.
Science-Backed Comfort and Pain Relief
Unlike footwear designed in isolation, our shoes are backed by real-world testing with people experiencing foot pain. This collaborative approach between our engineers and leading researchers creates solutions that address the root causes of discomfort.
Shop Science-Backed Comfort
Engineered for Optimal Comfort

Clinically Tested Footwear You'll Love



Real Relief for Real People



Shop by Category
Shop by Conditions
"Findings based on clinical studies conducted at Baylor College of Medicine and UNC-Chapel Hill’s Applied Biomechanics Lab.. Individual results may vary."
References:
[1] Finco MG, Ouattas A, El-Refaei N, Momin AS, Azarian M, Najafi B. Assessing the Acceptability and Effectiveness of a Novel Therapeutic Footwear in Reducing Foot Pain and Improving Function among Older Adults: A Crossover Randomized Controlled Trial. Gerontology. 2024;70(8):842-854. doi: 10.1159/000539307. Epub 2024 May 22. PMID: 38776890.
[2] UNC Quarterly Report (2023 Q2), Applied Biomechanics Laboratory, Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and North Carolina State University.
[3] Ouattas A, Finco MG, Dehghan Rouzi M, Azarian M, Rojas AZ, Bargas Ochoa M, El-Refaei N, Momin A, Najafi B. The role of therapeutic footwear to increase daily physical activity in older adults with chronic foot pain. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2025 Mar;123:106373. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2024.106373. Epub 2024 Oct 29. PMID: 39954566.